6 Practical Methods to Minimize HTTP Requests in WordPress
By Editorial Team |
Observing a WordPress website load slowly can be a significant source of frustration for site owners. Based on extensive experience managing numerous websites, many WordPress professionals have identified a common performance bottleneck: excessive HTTP requests.
Every request for a resource—whether an image, script, or stylesheet—contributes incrementally to the overall page load time. These small delays can accumulate, potentially leading to visitor abandonment. Fortunately, implementing effective optimizations does not require advanced development skills.
This guide outlines straightforward, actionable strategies that can substantially decrease the number of requests your site makes, resulting in a noticeably faster user experience.
The Importance of Reducing HTTP Requests
Slow-loading websites often suffer from an overload of individual resource requests. A typical WordPress page comprises numerous components—images, CSS, JavaScript, embedded media—that must be assembled by the browser to render the complete page.
Consider the browser as a courier tasked with fetching each piece of the page separately. This process becomes inefficient when a site contains many visual and interactive elements, each adding to the total load time.
Furthermore, modern websites frequently integrate external services such as analytics trackers or social media widgets. While these add functionality, they can introduce additional requests that, if not managed, degrade performance.
Unoptimized elements create unnecessary overhead, testing the patience of visitors who expect near-instantaneous loading. Research indicates that even minor delays can negatively impact conversion rates, user engagement, and overall satisfaction.

Therefore, streamlining HTTP requests is a critical performance optimization. Focusing on this area can enhance site speed, improve the user experience, and provide a competitive advantage. Performance optimization is both a technical necessity and a strategic business consideration.
Identifying HTTP Requests on Your Site
Before implementing reduction techniques, it is helpful to understand how to audit the requests your site currently generates.
Browser developer tools provide a clear view of all HTTP requests made when loading a page. This reveals every file required for page rendering.
In Google Chrome, access these tools via View » Developer » Inspect. Alternatively, right-click on the page and select 'Inspect' from the context menu.
Navigate to the 'Network' tab, then reload the page. A list will populate showing all loaded resources, including both internal and external requests.
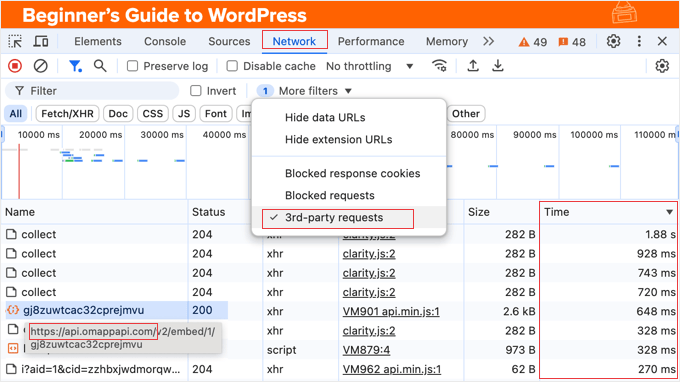
To isolate external requests, locate the filter toolbar within the Network panel and enable the '3rd-party requests' option. This will hide files served from your primary domain.
You can also filter by file type using the buttons at the top of the panel, allowing you to focus on specific resources like JavaScript (JS) or CSS files that affect loading behavior.
Pay attention to resources with long load times. The 'Time' column displays the duration for each request. Clicking this column header sorts the list, and clicking again will place the slowest-loading items at the top for easy review.
The 'Initiator' column may indicate which plugin or theme component triggered a particular request. Note any plugins or themes associated with slow-loading files for further investigation.
Third-party performance analysis tools can also provide detailed reports on request behavior. With this diagnostic knowledge, you can proceed to apply effective reduction strategies.
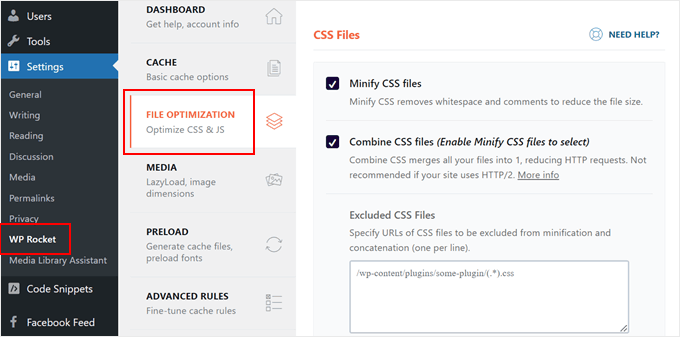
- Merge CSS and JavaScript Files
- Implement Lazy Loading for Media
- Utilize a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Configure Browser Caching
- Limit External Resource Dependencies
- Bonus: Activate Gzip Compression
1. Merge CSS and JavaScript Files
A highly effective method for reducing HTTP requests is to decrease the total number of files the browser must fetch. Combining multiple files into fewer, consolidated resources can achieve this without affecting functionality.
For instance, multiple CSS files governing various aspects of your site's design can be merged into a single stylesheet. This single file contains all necessary styling rules, requiring the browser to make one request instead of several.
The same principle applies to JavaScript files. Combining multiple scripts into one reduces the requests needed to load interactive features.
Several WordPress plugins can automate this file combination process. Popular solutions include both premium and free options designed for performance optimization.