11 Proven Strategies to Reduce DOM Size and Improve WordPress Performance
By Editorial Team |
The 'Avoid an excessive DOM size' alert in WordPress indicates that your webpage contains too many HTML elements, which can significantly slow down its loading speed.
Effective solutions include implementing performance optimization plugins, improving how images and galleries load, and selecting streamlined themes or page builders.
This warning commonly appears in Google Lighthouse and similar performance testing tools. While it may sound technical, the underlying principle is straightforward: when a website contains too many components, browsers struggle to process them efficiently.
Many WordPress professionals have successfully addressed this issue on high-traffic websites and helped numerous site owners enhance their performance metrics.
This guide presents 11 expert-recommended techniques to resolve DOM size problems and boost your WordPress site's overall performance.
Understanding the 'Avoid an Excessive DOM Size' Warning
The 'Avoid an excessive DOM size' notification appears in performance analysis tools when a webpage contains an excessive number of HTML elements that browsers must process.
DOM represents the Document Object Model, a hierarchical structure that organizes all elements on your webpage. Each component—whether a heading, paragraph, image, or interactive button—functions as a 'node' within this structure.
The collective count of these nodes determines the DOM size. When this number grows too large, browsers require additional time and computational resources to render the page, potentially slowing down your website.
Performance Impacts of Excessive DOM Size
An oversized DOM structure negatively affects WordPress website performance in several significant ways. Every element added to a page—from textual content and visual media to forms and navigation menus—increases the DOM node count.
This complexity produces the following consequences:
- Delayed Page Rendering: Browsers must parse the complete DOM structure before displaying page content. A more extensive structure requires longer processing time, delaying when visitors can view your content.
- Increased Memory Consumption: Complex DOM arrangements demand greater memory and processing capacity from users' devices. This effect becomes particularly noticeable on mobile devices with limited resources.
- Diminished User Experience: These performance limitations result in slower loading times. Visitors may become frustrated and abandon your site before content fully loads.
- SEO Disadvantages: Search engines like Google consider page speed when determining rankings. Slow-loading pages can negatively impact your search visibility and reduce conversion rates.
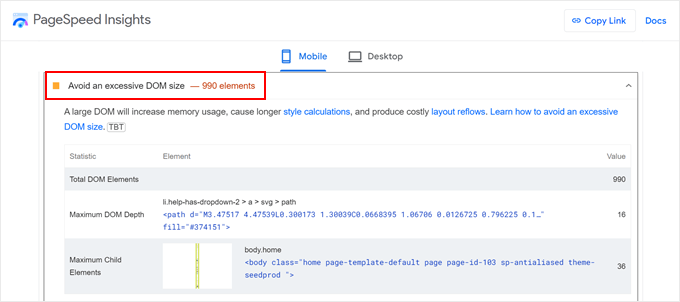
Google's DOM Size Thresholds
Testing applications such as Google Lighthouse evaluate multiple criteria rather than a single number when identifying excessive DOM size:
- Total DOM Nodes: A warning triggers when HTML elements (nodes) exceed 1,500. This represents the most frequent cause of DOM size warnings.
- Maximum DOM Depth: A warning activates when elements nest too deeply within each other. Lighthouse flags pages where nesting extends beyond 32 levels.
- Maximum Child Elements: A warning occurs when a single parent element contains more than 60 direct child elements. This situation often arises with poorly constructed mega menus or gallery displays.
Pages featuring multiple sliders, intricate layouts with numerous nested sections, or abundant embedded content frequently exceed these limits. Fortunately, you can address these issues without compromising design quality.
The following comprehensive guide presents 11 established methods for reducing DOM size and enhancing WordPress performance:
- Implement a WordPress Performance Optimization Plugin
- Evaluate Your Theme and Plugin Selection
- Select an Efficient Page Builder
- Optimize Visual Media Elements
- Configure Lazy Loading
- Paginate Extensive Comments or Content
- Minify CSS and JavaScript Resources
- Minimize Render-Blocking JavaScript and CSS
- Activate WordPress Caching
- Utilize a Content Delivery Network
- Optimize Your WordPress Database
Use the navigation links above to explore specific optimization approaches.
1. Implement a WordPress Performance Optimization Plugin
Our primary recommendation involves installing a robust WordPress performance optimization plugin. These tools manage the technical optimizations necessary for accelerating your website.
This approach allows you to concentrate on content creation and management while the plugin operates in the background.
Many experienced developers utilize performance plugins to handle caching, file optimization, and lazy loading implementation.
While primarily recognized as caching solutions, many performance plugins include features that address problems associated with large DOM structures. These capabilities typically encompass file optimization, lazy loading implementation, and JavaScript deferral.
We will examine these features in subsequent sections.
2. Evaluate Your Theme and Plugin Selection
While WordPress themes and plugins enhance functionality and visual presentation, they can also contribute to excessive DOM size.
Poorly developed themes and plugins may introduce unnecessary HTML elements, inflating your page structure. Similarly, plugins and themes containing unused features might still load their code, increasing DOM complexity.
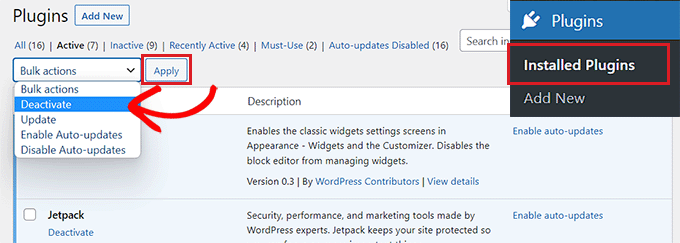
To identify whether specific plugins or themes cause the issue, deactivate plugins individually or temporarily switch to a default WordPress theme. After each modification, conduct speed tests to determine if DOM size warnings disappear.
To prevent this problem, consistently select themes and plugins from reputable sources such as the official WordPress directory or established developers. These providers typically maintain stricter coding standards.
3. Select an Efficient Page Builder
Page builders excel at creating custom layouts without coding knowledge, but some contribute to excessive DOM size. They frequently wrap content in additional HTML elements to control styling and layout arrangements.
For instance, a poorly optimized page builder might encase a single button within multiple nested <div> containers for alignment and styling purposes. Each container adds another node to the DOM, rapidly increasing the total count.
If you suspect your page builder causes the issue, test this theory by deactivating it on a staging site and rechecking DOM size. Built-in tools like the Full Site Editor offer alternatives, though they may provide less flexibility.
For optimal balance between flexibility and performance, consider using speed-optimized page builders that consistently outperform other popular options in performance testing.
Numerous established brands utilize performance-focused page builders for their website development needs.
4. Optimize Visual Media Elements
It's important to clarify how images relate to DOM size. The file size of an image (measured in KB or MB) doesn't affect DOM node count. An <img> tag represents a single node regardless of image file dimensions.
However, image presentation methods can increase DOM size. Some themes and gallery plugins wrap each image in multiple <div> containers for styling, lightbox functionality, or caption display. These additional wrapper elements—not the images themselves—contribute to DOM count.
While compressing images remains crucial for page speed optimization, you should also select gallery plugins that generate clean, efficient code. Specialized plugins can assist with both image compression and lazy loading implementation.
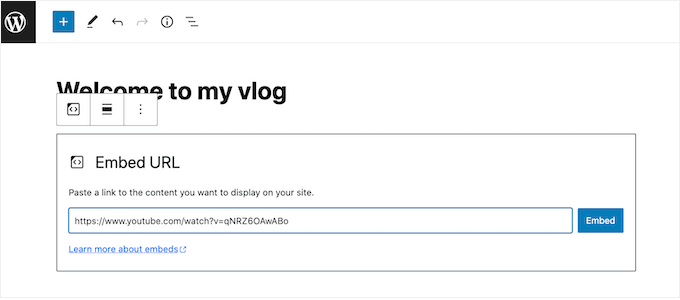
For video content, we recommend avoiding direct WordPress uploads. Instead, host videos on dedicated platforms like YouTube or Vimeo and embed them. This approach reduces server load and maintains cleaner DOM structure.