
Complete Guide: Migrating Your Website from Drupal to WordPress
Many website creators initially consider Drupal for their projects. While it offers robust capabilities, its complexity can present challenges, particularly for those new to web development. WordPress often emerges as a preferred alternative due to its intuitive interface and accessibility, leading numerous professionals to adopt it for their ongoing work.
Transitioning an entire website between platforms can understandably cause concern. The prospect of losing valuable content or disrupting functionality is a common worry during such migrations.
This comprehensive guide outlines a systematic approach to transferring your site from Drupal to WordPress securely and efficiently, based on methods widely used by experienced developers.
Reasons for Transitioning from Drupal to WordPress
Although Drupal and WordPress may appear similar at first glance, their operational approaches differ significantly in practice.
Drupal provides extensive functionality but can sometimes feel unnecessarily complex for routine tasks. Simple content modifications may require more time than expected, and locating qualified developers for adjustments can prove difficult or costly. The administrative interface might also seem daunting to some users.
WordPress typically offers a more straightforward user experience, making it a frequent recommendation for those seeking an accessible website platform. Consider it a versatile tool that's simple to master and logical in operation. Common activities like publishing articles, adding media to pages, or implementing basic forms become streamlined processes.
Conversely, Drupal functions more like specialized equipment—powerful and precise but potentially excessive for everyday requirements. Tasks that WordPress handles simply, such as creating custom page layouts, can become complicated in Drupal.
For detailed comparisons between these platforms, consult available resources discussing their respective strengths and limitations.
The following steps provide a reliable framework for moving your website from Drupal to WordPress:
- Step 1. Create Comprehensive Backups of Your Drupal Site
- Step 2. Install and Configure WordPress
- Step 3. Transfer Your Drupal Content
- Step 4. Redirect Your Domain to the New WordPress Site
- Step 5. Configure Permalinks and URL Redirects
- Step 6. Select and Customize Your WordPress Theme
- Step 7. Add Necessary WordPress Plugins
- Additional Guidance: Learning WordPress Fundamentals
- Common Questions About Drupal to WordPress Migration
- Post-Migration Recommendations
Step 1. Create Comprehensive Backups of Your Drupal Site
Before initiating any migration procedures, establish complete backups of your existing Drupal installation.
Additionally, document your current URL structure. This information will prove valuable later for maintaining search engine visibility.
Backing Up with Drupal Modules
You can efficiently back up your Drupal website using dedicated modules, though manual methods remain available for technically proficient users.
The simplest approach involves the free Backup and Migrate module, which simplifies the backup process considerably.
Begin by downloading the module from official sources. After obtaining the compressed file, access your Drupal administration panel and select Extend from the navigation menu.
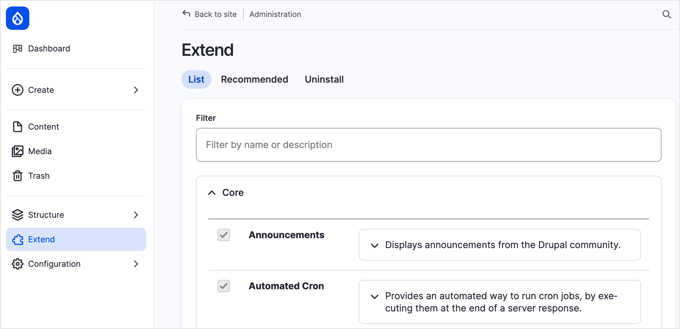
Click the + Install new module button.
On the subsequent screen, upload the downloaded file. Following successful installation, return to the primary Extend section.
Scroll through the module listings until locating 'Backup and Migrate' (typically categorized under 'Other'). Select the adjacent checkbox and click the installation button at the page bottom.
Once activated, this module becomes accessible through your administration menu, enabling backups of databases, files, or complete site data.
Manual Backup Procedures
For those comfortable with technical processes, manual backup methods provide an alternative approach.
First, preserve your website files using your hosting provider's file management tools or FTP software.
Within your hosting account's file manager, navigate to your site's root directory, commonly labeled public_html or www. Right-click this folder and choose the compression option from the contextual menu.
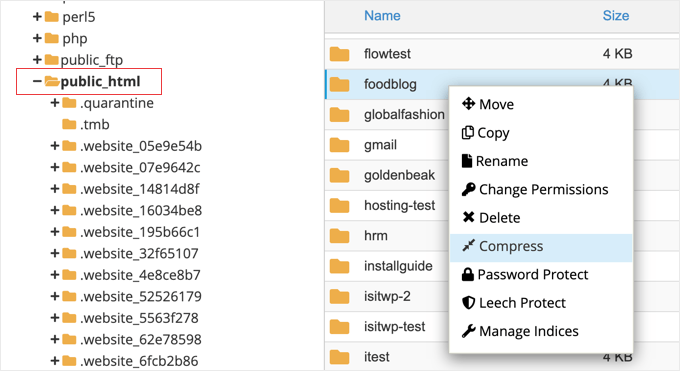
When prompted for compression format, select 'Zip Archive'. After compression completes, dismiss the confirmation notification.
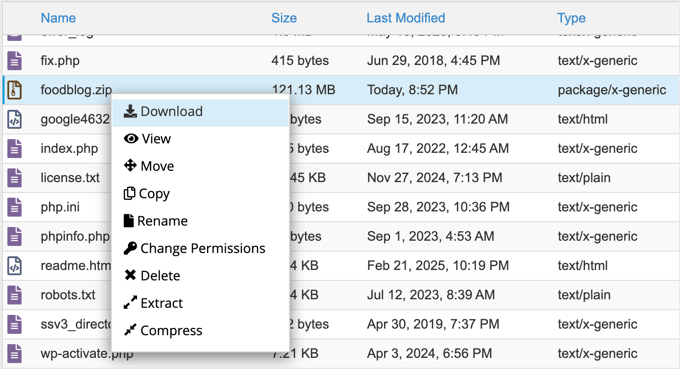
Locate the newly created zip file within the public_html directory. Right-click the file and choose 'Download', storing this backup in a secure location.
Next, back up your database using phpMyAdmin, available through most hosting provider dashboards.
For instance, many hosting services include phpMyAdmin within their hosting management sections.
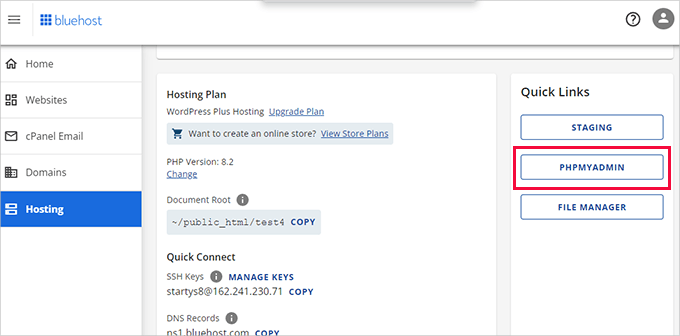
Clicking the phpMyAdmin link typically opens the application in a new browser window.
Select your Drupal database from the left panel, then click the 'Export' button at the top.
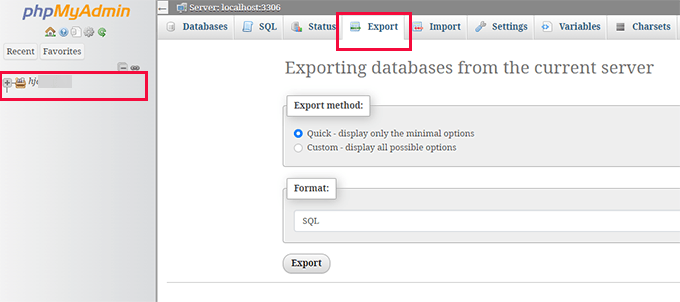
When selecting export methodology, choose 'Custom' to display all database tables associated with your Drupal installation.
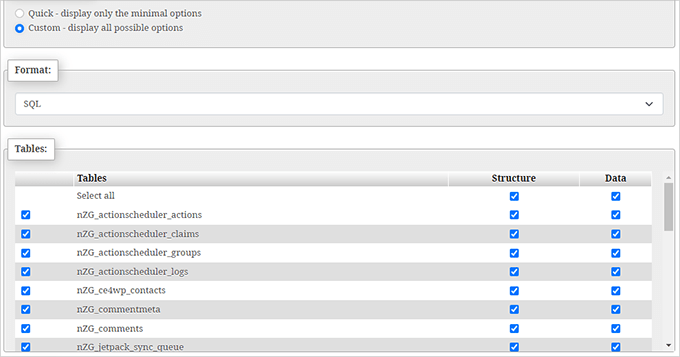
Ensure all tables remain selected for a complete backup.
Note: Your specific table names will differ from examples shown, potentially including designations like node or taxonomy_term_data, though the export process remains identical.
Scroll to the 'Output' section and enable the 'Save output to a file' option.
Select 'zipped' for compression preferences.
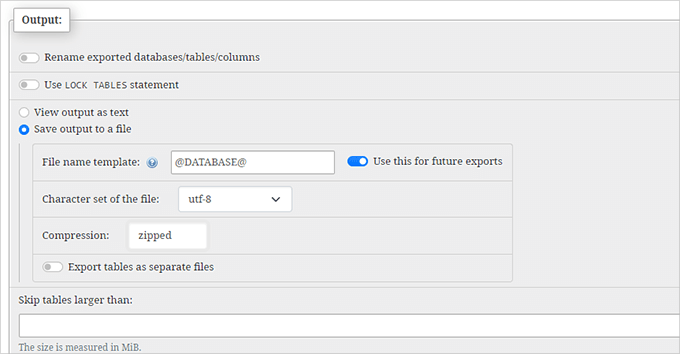
Finally, navigate to the page bottom and click 'Go'.
The compressed database file will download to your computer for secure storage alongside your file backup.
Documenting URL Structures
Preserving your link architecture is crucial for search engine optimization and maintaining content accessibility.
Compile a comprehensive list of existing Drupal URLs to facilitate redirect configuration in WordPress. This ensures visitors clicking legacy links automatically reach appropriate pages on your new WordPress site.
Many developers utilize browser extensions like Link Klipper for Chrome, which efficiently extracts all links from websites. Install this or similar tools through browser extension repositories.
Visit your Drupal homepage in Chrome, then click the extension icon in your toolbar and select 'Extract All Links'.


