
A Comprehensive Guide to Migrating Your Website from Drupal to WordPress
Many website builders initially consider Drupal for its robust capabilities. However, its complexity and steep learning curve can be challenging, especially for those new to content management systems. WordPress often emerges as a preferred alternative due to its intuitive interface and accessibility, making it a popular choice for countless projects.
Transitioning an entire website between platforms can understandably cause concern about potential data loss or functionality issues. This guide provides a systematic approach to ensure a smooth and secure migration process.
Reasons for Transitioning from Drupal to WordPress
While Drupal and WordPress share some similarities as website platforms, their operational experiences differ significantly. Drupal offers extensive power and customization but can sometimes introduce unnecessary complexity for routine tasks. Simple content updates may become time-consuming, and finding specialized developers can be difficult and costly. The administrative interface may also feel overwhelming to some users.
WordPress is widely recognized for its user-friendly design, making it a frequent recommendation for those seeking an efficient website solution. It functions like a versatile, everyday tool that is straightforward to operate. Common activities such as publishing blog posts, adding media to pages, or implementing basic forms are typically simple to accomplish.
In contrast, Drupal resembles a specialized instrument kit—extremely capable for specific applications but potentially excessive for standard requirements. Tasks that are simple in WordPress, like creating custom page layouts, can require more technical effort in Drupal.
The following steps outline a reliable method for transferring your website from Drupal to WordPress:
- Step 1. Create Backups of Your Drupal Site and URL Structure
- Step 2. Install and Configure WordPress
- Step 3. Transfer Your Drupal Content
- Step 4. Redirect Your Domain to the New WordPress Site
- Step 5. Configure Permalinks and URL Redirects
- Step 6. Select and Set Up a WordPress Theme
- Step 7. Install Important WordPress Plugins
- Additional Guidance: Learning WordPress
- Frequently Asked Questions About Drupal to WordPress Migration
- Post-Migration Steps
Step 1. Create Backups of Your Drupal Site and URL Structure
Before initiating any migration procedures, it is essential to create complete backups of your existing Drupal installation. Additionally, documenting your current URL structure is crucial for preserving search engine rankings during the transition.
Backing Up Your Drupal Site Using a Module
The simplest approach for most users involves employing a dedicated module, while technically proficient individuals may opt for manual methods.
The free Backup and Migrate module offers a straightforward solution for safeguarding your Drupal data. Begin by downloading the module from the official repository. After obtaining the compressed file, access your Drupal administration panel and select Extend from the main navigation.
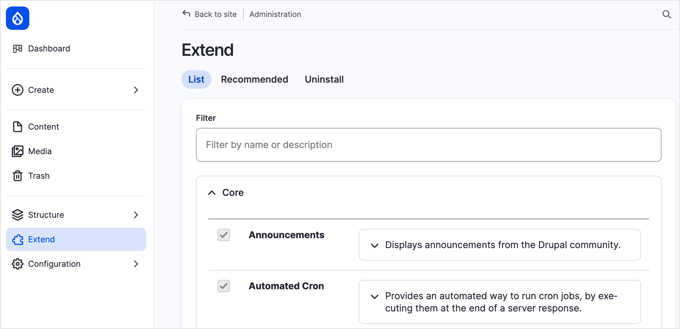
Click the + Install new module button, then upload the downloaded file on the subsequent screen. Following successful installation, return to the Extend page, locate the ‘Backup and Migrate’ module (typically in the ‘Other’ category), enable it, and proceed with installation.
Once activated, the module will appear in your administration menu, allowing you to create comprehensive backups of your database, files, or both components.
Manual Backup Procedures for Drupal
For those comfortable with technical processes, manual backup provides an alternative method.
First, secure your website files using your hosting provider’s file management interface or FTP client. Navigate to your site’s root directory (commonly named public_html or www), right-click the folder, and select the compression option.
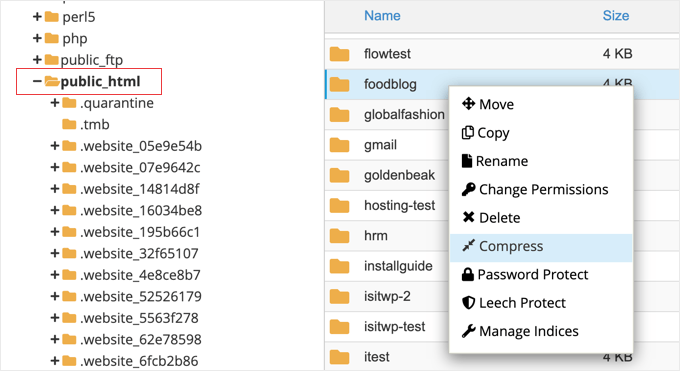
Choose ‘Zip Archive’ as the compression format. After completion, locate the compressed file within the public_html directory, right-click it, and download it to a secure local storage location.
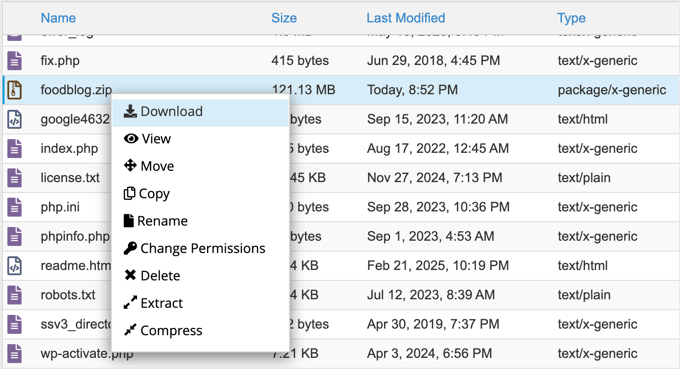
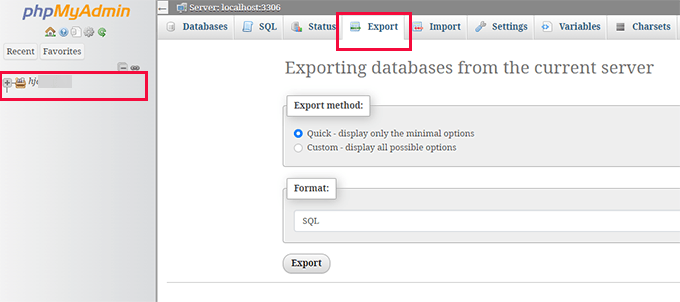
Next, back up your database using phpMyAdmin, available through most hosting control panels. Access the tool, select your Drupal database from the left sidebar, and click the ‘Export’ button.
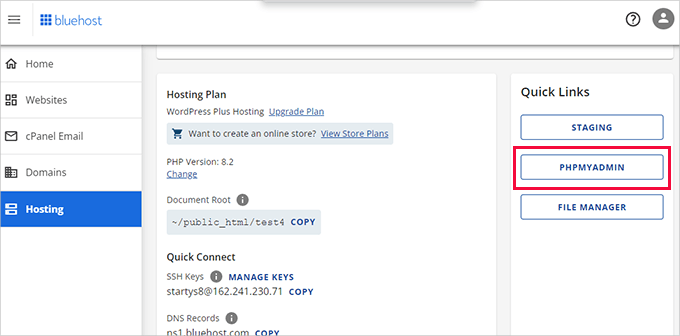
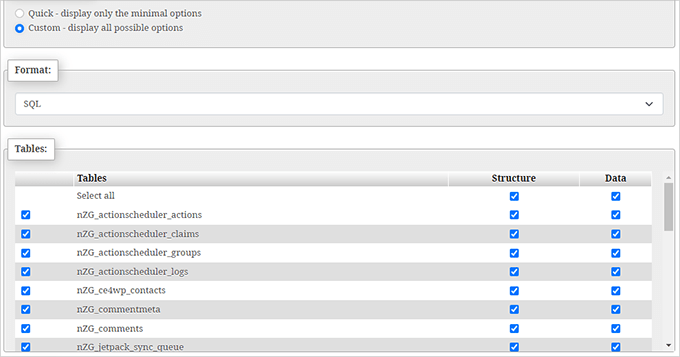
Choose ‘Custom’ as the export method to display all database tables. Ensure every table is selected for a complete backup. Note that your table names will differ from examples, containing Drupal-specific identifiers like node or taxonomy_term_data, but the export process remains identical.
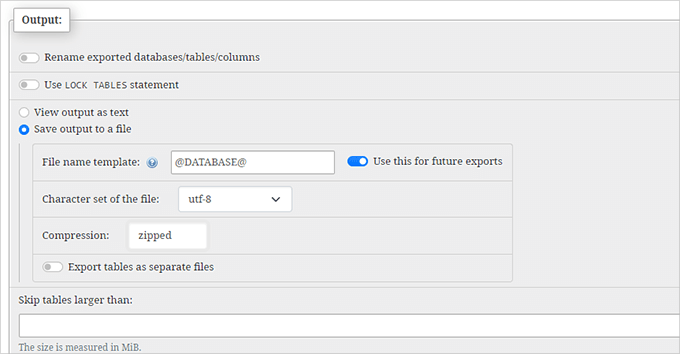
Scroll to the ‘Output’ section, select ‘Save output to a file’, and choose ‘zipped’ compression.
Finally, click ‘Go’ to download the compressed database file. Store this securely alongside your file backup.
Documenting Your URL Structure
Preserving your link structure is vital for maintaining SEO value and ensuring visitors can access content through existing links. Compile a complete list of your current Drupal URLs to facilitate proper redirect configuration in WordPress. This ensures that any requests to old Drupal addresses automatically redirect to corresponding pages on the new WordPress site.
Many experienced developers recommend using browser extensions like Link Klipper for Chrome, which efficiently extracts all links from a website. After installing the extension, visit your Drupal homepage and activate the link extraction feature.


