
Resolving the WordPress Admin Ajax 400 Bad Request Error: A Comprehensive Guide
Encountering errors in WordPress can be challenging, particularly when the error message provides limited information for troubleshooting.
The admin Ajax 400 (Bad Request) error typically indicates that your web server could not properly interpret a request from your browser. This issue frequently arises due to conflicts with plugins, themes, or even minor URL discrepancies.
Many WordPress administrators have reported this error occurring during file uploads, when executing custom code, or while navigating the WordPress admin interface. Fortunately, resolving this error is generally straightforward with the right approach.
This guide will explain the common causes of the 400 error and provide practical solutions to address it efficiently.
Understanding the 400 (Bad Request) Error
The 400 (Bad Request) error typically occurs when a web browser sends a request that the server cannot process due to malformed syntax or invalid parameters.
While this is a common WordPress error, the generic nature of the message often makes initial troubleshooting difficult for users without technical experience.
You may encounter this error displayed as a simple '400 Bad Request' message in your browser window. The exact appearance can vary depending on your hosting provider's configuration.
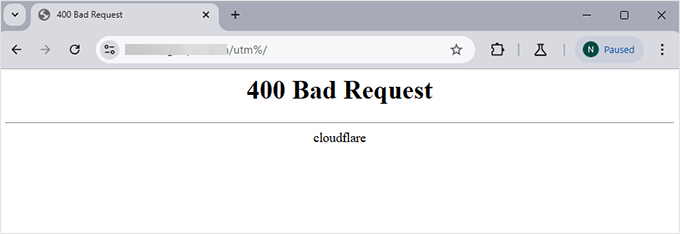
The error may also appear in your browser's developer tools within the 'Console' section.
This is particularly common when the request involves the admin-ajax.php file, which handles Ajax requests in WordPress.
Here are the most frequent causes of this error according to experienced WordPress developers:
1. Incorrect or Malformed URL
Minor typographical errors or additional characters in a URL can cause server rejection. Even a misplaced space or symbol can trigger this error.
2. Browser Cache and Cookies Issues
Outdated or corrupted browser data represents another common trigger. Many users have resolved this error simply by clearing their browser cache and cookies.
3. Excessive File Upload Size
Attempting to upload files that exceed server-imposed size limitations can also result in a 400 error. This frequently occurs when uploading high-resolution media files.
4. Plugin or Theme Compatibility Problems
Newly installed or recently updated plugins and themes may contain code that conflicts with your WordPress configuration, potentially triggering a 400 error upon activation.
5. Server Configuration Problems
Occasionally, the issue originates from server-side configurations. A corrupted .htaccess file or misconfigured server settings can cause this error, though restoring default configurations typically resolves it.
Now that we've identified potential causes, let's proceed through systematic troubleshooting steps.
Step-by-Step Solutions for the 400 (Bad Request) Error
Having examined the potential causes of the 400 (Bad Request) Error, we will now explore practical solutions. These methods are effective and accessible even for users with limited technical expertise.
The following steps will guide you through the resolution process:
- Verify the URL
- Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
- Adjust File Upload Size
- Deactivate All Plugins
- Switch to a Default Theme
- Reset Permalinks
- Additional Troubleshooting Resources
1. Verify the URL
Begin by examining the URL you're attempting to access. Even minor typographical errors, such as missing characters or misplaced spaces, can disrupt the request and generate a 400 error.
Ensure the link is accurate and free from extraneous symbols or spaces. If the URL appears correct but the error persists, proceed to the next troubleshooting step.
2. Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
Outdated or corrupted browser data frequently causes 400 Bad Request errors. Clearing your cache and cookies represents a quick initial solution.
For Chrome Users: Click the three-dot menu in the upper right corner and select 'Delete browsing data.'
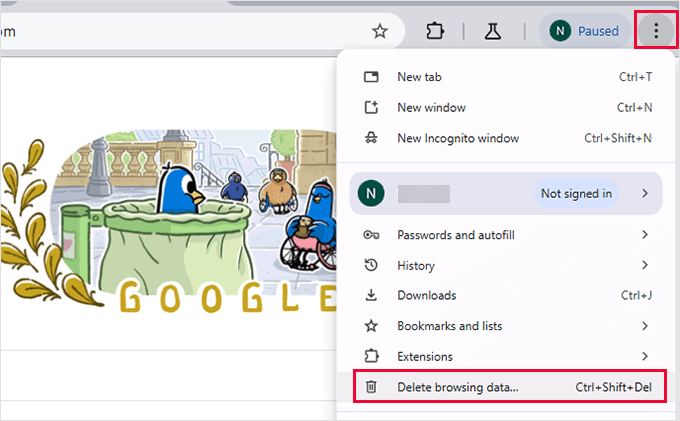
In the dialog window, select both 'Cookies and other site data' and 'Cached images and files.'
Set the time range to 'All time,' then click 'Delete data.'
For Firefox Users: Click the menu icon in the upper right corner of the browser window.
From the menu, select 'Settings.'

This action opens the browser settings interface.
Navigate to the 'Privacy & Security' tab, scroll to 'Cookies and Site Data,' and click 'Clear Data.'
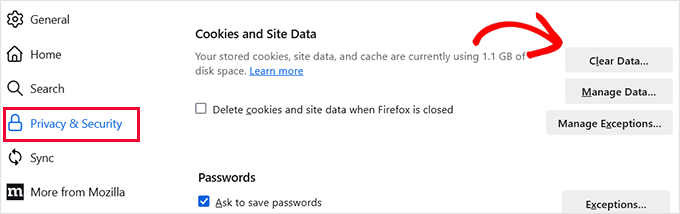
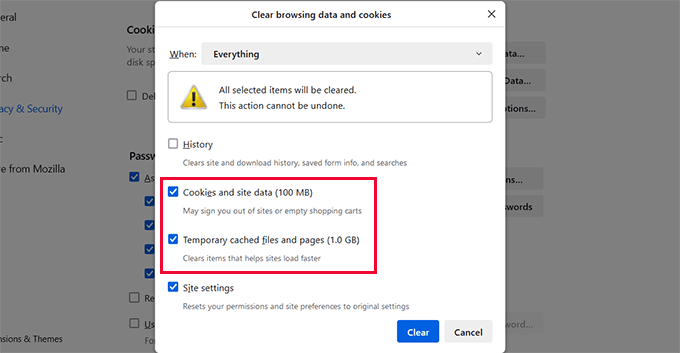
Select both 'Cookies and site data' and 'Cached web content.'
For the time range, choose 'Everything' and then click 'Clear.'
For alternative browsers, consult documentation regarding cache clearing procedures for your specific browser.
After clearing the cache, refresh your website to determine if the error has been resolved.
3. Adjust File Upload Size
If the error occurs during file upload attempts, the file size may exceed your server's configured limits.
Consider these approaches to address this issue:
- For images, optimize them for web delivery using compression tools
- If you regularly upload large files, investigate methods for handling substantial media files within WordPress
- When compression proves insufficient, consider increasing your site's memory allocation by adding this directive to your wp-config.php file:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');After implementing these changes, attempt the upload again to verify error resolution.
4. Deactivate All Plugins
Plugin conflicts represent another frequent cause of the admin Ajax 400 error, often resulting from incompatible or poorly coded extensions.
To identify problematic plugins, begin by deactivating all installed plugins.
Navigate to Plugins » Installed Plugins in your WordPress dashboard. Select all plugins, choose 'Deactivate' from the Bulk Actions dropdown menu, and click 'Apply.'
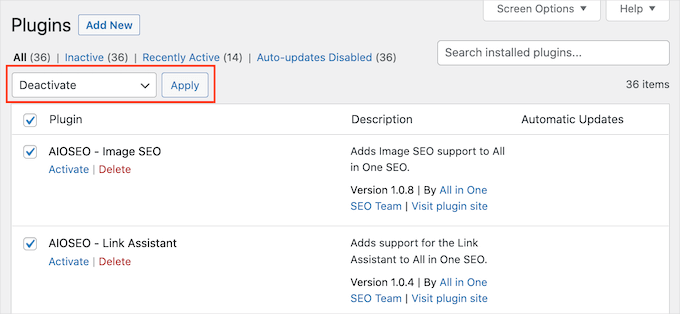
Following deactivation, visit your website to determine if the error has disappeared. If resolved, a plugin conflict was likely the cause.
Begin reactivating plugins individually. After each activation, check your website until you identify the specific plugin triggering the error.
Important Note: If you cannot access the WordPress admin area, you can deactivate plugins using FTP or your hosting control panel's file management tools.


