
Targeted CSS Implementation for WordPress User Roles: A Practical Guide
Many WordPress professionals encounter situations where different user groups require distinct visual experiences. Premium members might benefit from streamlined interfaces, content creators often need reduced distractions, and customers typically shouldn't see administrative elements.
WordPress doesn't include native functionality for applying styles based on user roles. When you need to hide elements, modify layouts, or adjust designs for specific user categories, the default approach involves editing theme files or implementing custom code.
This approach carries significant risks. Numerous site administrators have inadvertently broken their websites by placing CSS snippets incorrectly, particularly when working directly within theme or child theme files.
The most secure and straightforward method for applying CSS according to user roles involves utilizing a dedicated code management plugin with conditional logic capabilities. This approach allows targeting roles such as Administrators, Editors, or Subscribers without modifying theme files directly.
This guide demonstrates how to implement custom CSS for specific user roles using an accessible tool. This methodology represents the standard approach employed by experienced developers when requiring a reliable, safe solution that prevents future complications.
This guide covers the following essential topics:
- Purpose and Applications of Role-Based CSS in WordPress
- Implementing Custom CSS for Specific User Roles
- Applying Custom CSS in Different Site Areas
- Common Questions
- Further Resources
Purpose and Applications of Role-Based CSS in WordPress
Website administrators managing multiple sites with user login functionality frequently encounter the need to customize visual presentation for different user categories.
Testing has consistently shown that personalized interfaces significantly enhance user engagement. Industry research indicates that tailored web experiences can improve conversion metrics by approximately 10-15%, making role-specific styling a valuable strategic consideration.
Enhanced user experience typically results in increased satisfaction and improved performance metrics.
Whether you manage websites, develop solutions, or design interfaces, controlling visual presentation for different user groups provides substantial benefits.
Common implementation scenarios include:
- Membership Platforms: Custom CSS enables distinct experiences for premium members versus standard users.
- Online Stores: You can emphasize shopping carts, loyalty discounts, and special offers for authenticated customers.
- Multi-Author Publications: Managing publications with numerous contributors becomes more efficient with customized interfaces. CSS modifications can create streamlined editing environments while maintaining simplicity for contributors and subscribers.
- Client Websites: You can simplify administrative interfaces for clients by concealing specific elements through CSS. This approach proves particularly valuable for minimizing confusion by hiding complex dashboard components or plugin notifications that might overwhelm non-technical users.
The primary challenge involves instructing WordPress which CSS rules to implement for different user categories.
Implementing Custom CSS for Specific User Roles
The most efficient method for managing custom code, including CSS modifications, involves using a dedicated code management plugin. This approach provides secure management of custom CSS within a centralized location.
Note: Several plugins offer free versions with basic functionality, though premium plans typically unlock advanced features.
Benefits of specialized code management plugins:
- They enable safe implementation of custom code, including CSS modifications, without risking website stability. If a code snippet causes issues, you can easily deactivate it.
- They include sophisticated code insertion and conditional logic capabilities, allowing snippets to execute only under specified conditions.
- They often provide extensive code libraries containing useful snippets, reducing the need for multiple separate plugins.
Let's examine the process for adding custom CSS targeting a specific user role.
Creating a Custom CSS Snippet
For this demonstration, we'll customize the WordPress Administrative Dashboard for a specific role (such as Editor). We'll implement code that emphasizes the 'Posts' menu in the backend to illustrate the methodology.
- First, install and activate your chosen code management plugin. Refer to standard WordPress plugin installation procedures if needed.
- After activation, navigate to the Code Snippets » + Add Snippet section.
- Locate the 'Add Your Custom Code' option and select '+ Add Custom Snippet'.
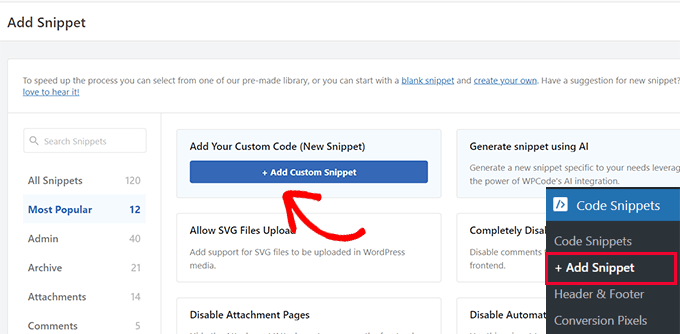
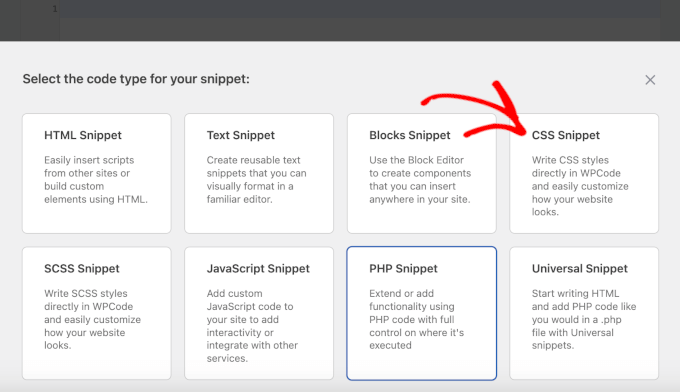
- On the configuration screen, choose 'CSS Snippet' as the code type from the dropdown menu (the default is typically HTML Snippet).
- Provide a descriptive title for your snippet, such as "Administrative Menu Highlight for Editors."
- Insert your custom CSS into the 'Code Preview' area.
Here's the sample code for this administrative interface example:
li#menu-posts { background-color: #bf0505; }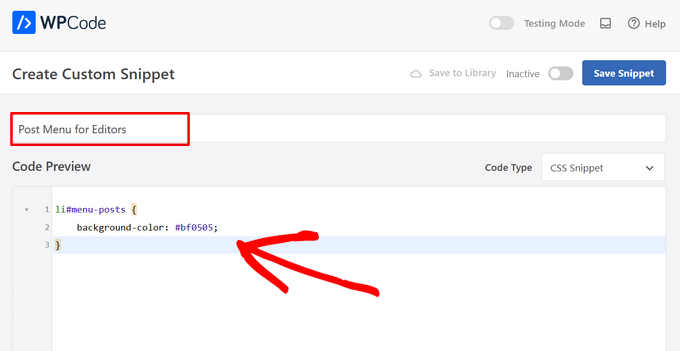
Important: Configuring the Correct Insertion Location
Since this particular code targets the Administrative Dashboard, you must navigate to the 'Insertion' section and select 'Admin Header' as the insertion point.
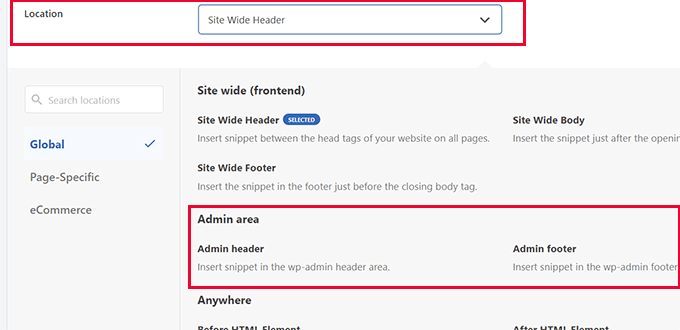
If you were implementing CSS for your site's public-facing pages (such as member areas), you would maintain the default 'Site Wide Header' location.
Implementing Conditional Logic
Now, let's ensure this code executes exclusively for the intended user role.
- Navigate to the 'Conditional Logic' section and activate the 'Enable Logic' option.
- Configure the 'Condition' to 'Show' and select '+ Add new group'.
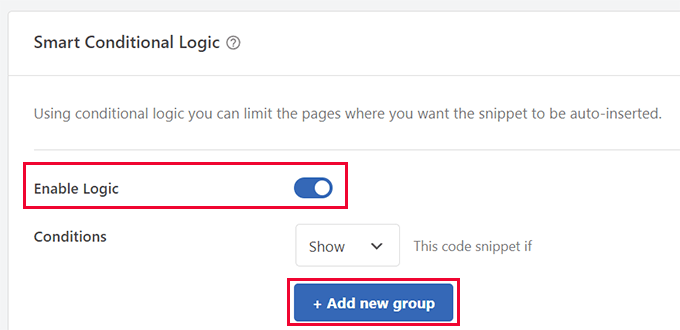
- Choose 'User Role' from the available options list.
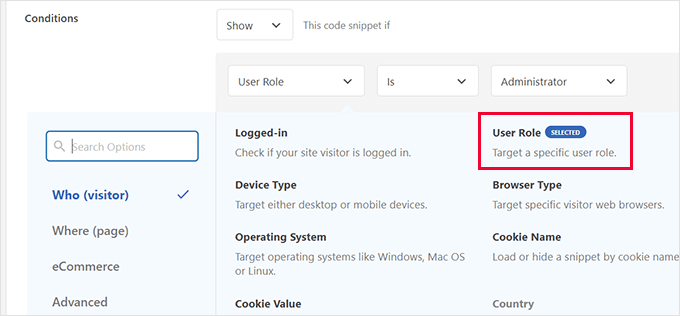
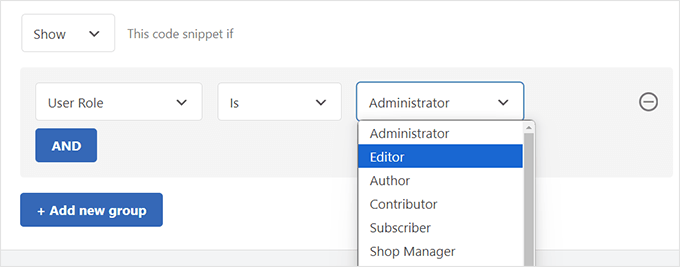
- Select the specific role you wish to target (for example, Editor or Subscriber).
- Finally, select 'Save Snippet' in the upper-right corner and change the status from 'Inactive' to 'Active'.


