A Professional Guide to Crafting WordPress Maintenance Reports for Clients
Managing a WordPress service business involves two critical responsibilities: ensuring client websites operate reliably and effectively communicating the ongoing maintenance work performed.
The challenge many professionals face is that clients often take for granted the routine updates, security scans, and performance enhancements that keep their sites functioning optimally. They simply expect seamless operation without understanding the technical efforts involved.
This guide provides a straightforward approach to developing maintenance reports that clients will actually review and appreciate. You'll learn to create clear, professional documentation that highlights your work without creating additional administrative burdens.
The Value of Maintenance Reports for Client Relationships
Regular WordPress maintenance documentation serves purposes beyond mere formality. These reports enhance communication with clients, demonstrate your technical expertise, and illustrate the ongoing value of your maintenance services.
By keeping clients informed about website health and maintenance activities, you can establish trust and foster stronger long-term partnerships.
Clients entrust you with their WordPress websites, often without fully comprehending the technical work required. Detailed reports help bridge this knowledge gap by clearly presenting the behind-the-scenes work, thereby reinforcing their confidence in your capabilities.
Thorough documentation of each maintenance activity demonstrates accountability. Clients appreciate knowing that you proactively maintain their site's health, providing them with assurance that their digital assets are properly managed.
Now, let's examine what elements to include in WordPress website maintenance reports for clients.
Essential Components of a Client Maintenance Report
When developing client maintenance reports, there might be a temptation to include every technical detail.
However, the report's primary purpose is to provide clients with a concise overview of completed work while highlighting metrics relevant to their business objectives.
Here are several important elements to incorporate in your reports:
- Security Updates: While clients may not understand technical terminology, they certainly care about security. Briefly mention updates to WordPress core, themes, and plugins. Explain how these updates address vulnerabilities and protect the site from potential threats.
- Backups: Provide reassurance that client data remains secure. Describe your backup procedures using straightforward language – including frequency and storage locations. To build additional confidence, mention whether backups are stored off-site or in cloud services.
- Performance Optimization: Website speed directly influences user experience and search engine visibility. In your report, briefly explain optimization measures taken, including plugin updates, image compression, database maintenance, or other technical adjustments.
- Uptime Monitoring: If you monitor website availability, share the overall uptime percentage. Explain why consistent uptime matters for visitor retention and search engine rankings.
- Additional Services: Finally, document any supplementary work completed. This might include troubleshooting, content modifications, new publications, landing page improvements, or feature implementations.
With these components in mind, let's explore how to create a WordPress maintenance report for your clients. Here's a brief overview of topics covered in this guide:
- Creating a Maintenance Report in WordPress
- Frequently Asked Questions About WordPress Maintenance
- Additional Resources on WordPress Maintenance
Let's begin.
Creating a Maintenance Report in WordPress
The most efficient method for delivering WordPress maintenance reports to clients involves using specialized plugins designed for this purpose.
These tools are particularly useful for freelancers, agencies, and website managers who need to generate client-friendly documentation.
Many reporting plugins automatically track updates made to plugins, themes, and WordPress core files. While they handle technical change logs automatically, you can still manually include notes about other metrics like uptime and backup procedures.
For this demonstration, we'll use a freely available reporting plugin that meets most users' requirements.
Premium versions often provide advanced customization features, including white-labeling options that allow you to incorporate your branding, remove plugin identifiers, schedule automatic report delivery, and integrate with additional tools.
First, you'll need to install and activate your chosen reporting plugin. From your WordPress dashboard, navigate to Plugins and select Add New Plugin.
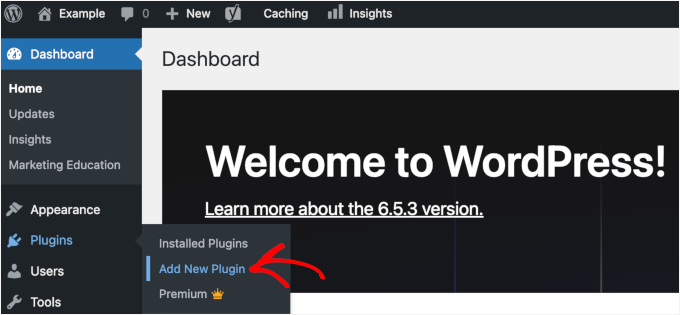
You can then use the search functionality to locate the plugin quickly.
Proceed by clicking the installation option in the search results.
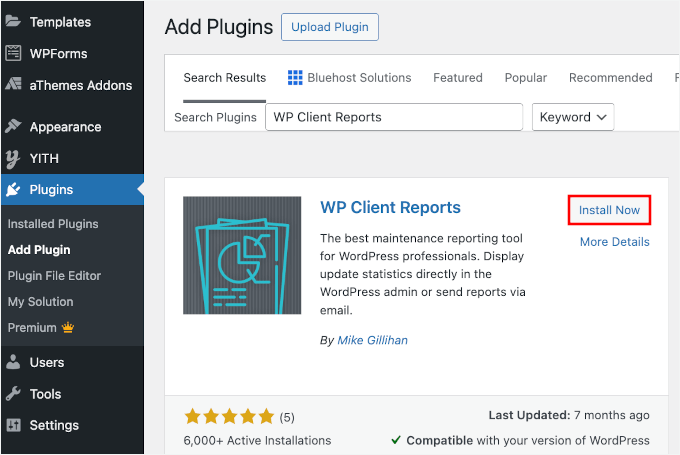
Remember to activate the plugin when prompted. If you require assistance, numerous online resources provide guidance on WordPress plugin installation.
After activation, access the plugin settings through your WordPress administration area. Here, you'll configure email settings for your reports.
You can customize the report subject line, specify recipient email addresses, define the sender email address, and adjust other relevant parameters.
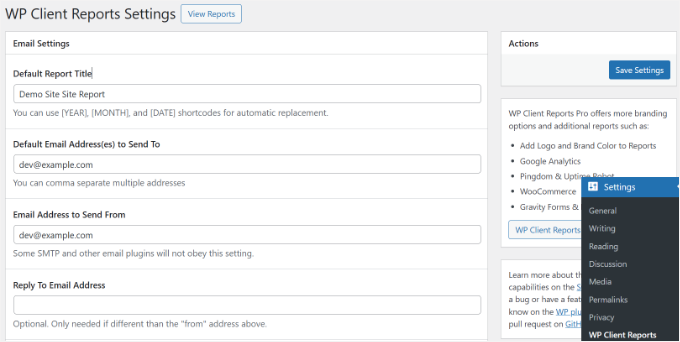
Scrolling further reveals additional options, including site identification, email introduction text, and footer customization.
You'll also find settings for tracking software updates and site content modifications. Ensure these tracking features remain enabled.
Once configured, save your settings.
You can now access client reports through the appropriate administration section.
Reports can display the total number of updates implemented on client websites.
These include WordPress core updates, plugin updates, and theme modifications. Most plugins allow date range selection to display statistics from specific periods.
Typically, maintenance statistics from the previous 30 days appear by default.
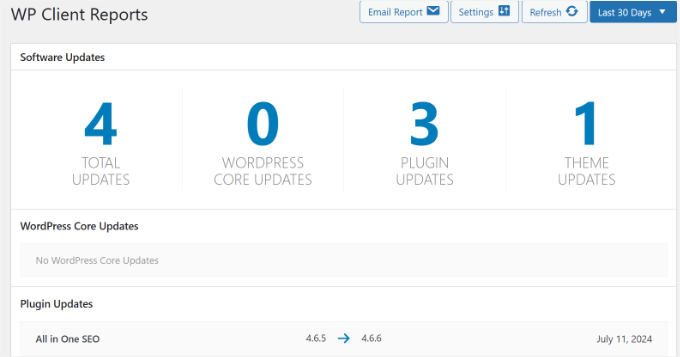
The most valuable feature of these reporting tools is their ability to display which specific files, plugins, and themes received updates, along with their previous and current version numbers.


